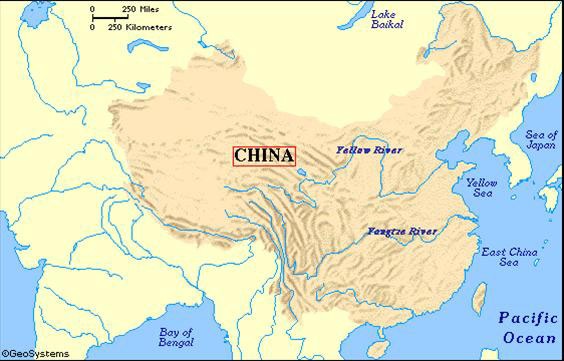
China is one of the largest countries in the world apart from being one of the most populous countries in the world. It is the home to the one-fifth of the world’s population. In Ancient China Geography, occupying the eastern portion of the Asian continent, the vast land stretches from over 50 degrees latitude and over 62 degrees longitude, having a total land area of more than 9.5m sq km. The official name of China is the Peoples Republic of China. The total land boundary is of 22,117km.
Ancient China was blessed with a variety of climates and terrains. It had the cold temperate zones, as well as the equatorial belt, also passed through its territory. Ancient Chinas land, as well as present Chinas land, is covered with forests, grasslands, plains, and hills. It is blessed with worlds driest deserts, highest mountains and also some of the best arable land.

The southern China was wet and tropical whereas the north-west China was covered with dessert. In the remote north-east, where it comes close to its neighbor Russia, the temperature drops down to as low as -50 degrees approx. in winter.
As stated above that, on one hand, China is home to one of the worlds highest mountains which are situated in the western region, on the other hand, its lowest point is in Turfan Depression, at -154 meters below sea level.
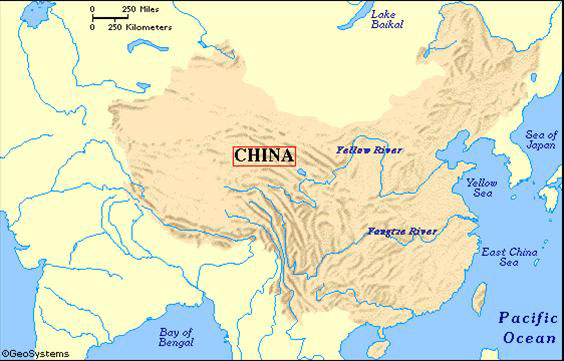
The incredible heat of the Turfan Depression makes it also known as one of the furnaces of China. The headwaters of the two most important rivers of China, namely, the Yellow River and the Yangzi river, is created by the melting snow of the mountains in the west.
The yellow windborne clay dust, called loess gave the Yellow River its name which blows across the northern China from the steppes of Central Asia. It was the loess only which blow in the river and gave its yellow color to it. The vast rice-growing region in the southern China was irrigated by its next important river, namely, the Yangzi River.